AMD Ryzen 9 9950X vs Intel Core i9-14900K: Full Review, Gaming Benchmarks, and Best Choice for 2025
AMD Ryzen 9 9950X vs Intel Core i9-14900K: Which High-End CPU Wins in 2025?
When enthusiasts discuss building the ultimate gaming or workstation PC in 2025, two processors stand at the very top: AMD’s Ryzen 9 9950X and Intel’s Core i9-14900K. Both chips push their architectures to the limits, offering extraordinary speeds, massive core counts, and advanced features that appeal to gamers, content creators, and power users alike.
Choosing between them is no simple task. While both CPUs promise elite performance, the way they achieve it — and the specific strengths they offer — vary significantly. In this article, we will take an in-depth look at their specifications, gaming benchmarks, productivity performance, thermal behavior, platform differences, and overall value to help you make the right decision.
Specifications Overview
AMD’s Ryzen 9 9950X is built on the company’s new Zen 5 architecture, leveraging a refined 4nm process node. It features 16 cores and 32 threads, with a base clock speed of 4.3 GHz and a maximum boost clock reaching up to 5.7 GHz. AMD has heavily optimized Zen 5 to deliver not just raw speed, but better power efficiency and improved IPC (instructions per clock) performance compared to previous generations.
On the other hand, Intel’s Core i9-14900K is based on the Raptor Lake Refresh architecture, still utilizing the Intel 7 (10nm Enhanced SuperFin) process. It incorporates a hybrid design with 8 performance cores and 16 efficiency cores, totaling 24 cores and 32 threads. The 14900K can reach a boost clock speed of up to 6.0 GHz under ideal conditions, representing one of the highest clock speeds ever achieved in a consumer-grade CPU.
| CPU | Cores/Threads | Base Clock | Boost Clock | Cache | TDP | MSRP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AMD Ryzen 9 9950X | 16/32 | 4.3 GHz | 5.7 GHz | 80 MB L3 Cache | 170W | $699 |
| Intel Core i9-14900K | 24/32 | 3.2 GHz (P-core) | 6.0 GHz | 36 MB L3 Cache | 125W (253W PL2) | $589 |
Gaming Performance
In gaming, Intel has long held a slight edge, especially at lower resolutions like 1080p where CPU bottlenecks are more apparent. The Intel Core i9-14900K continues this trend, offering the highest frame rates in competitive esports titles such as Counter-Strike 2, Valorant, and Fortnite. Thanks to its extremely high single-threaded performance and superior boost clocks, the 14900K can outperform the Ryzen 9 9950X by a margin of approximately 3–5% in certain gaming scenarios.
However, the gap is minimal, and at 1440p and 4K resolutions, the differences become even narrower. In graphically demanding AAA games like Cyberpunk 2077, Baldur’s Gate 3, and Alan Wake 2, the Ryzen 9 9950X often matches or even slightly outperforms the Intel Core i9-14900K in frame times and minimum FPS, thanks to its uniform 16 high-performance cores.
| Game Title | Resolution | AMD Ryzen 9 9950X Avg FPS | Intel Core i9-14900K Avg FPS |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cyberpunk 2077 | 1080p | 168 FPS | 173 FPS |
| Cyberpunk 2077 | 1440p | 134 FPS | 132 FPS |
| Cyberpunk 2077 | 4K | 82 FPS | 81 FPS |
| Fortnite | 1080p | 414 FPS | 437 FPS |
| Fortnite | 1440p | 367 FPS | 370 FPS |
| Fortnite | 4K | 244 FPS | 245 FPS |
| Call of Duty: Modern Warfare III | 1080p | 222 FPS | 229 FPS |
| Call of Duty: Modern Warfare III | 1440p | 186 FPS | 190 FPS |
| Call of Duty: Modern Warfare III | 4K | 129 FPS | 130 FPS |
| Baldur’s Gate 3 | 1080p | 180 FPS | 178 FPS |
| Baldur’s Gate 3 | 1440p | 155 FPS | 153 FPS |
| Baldur’s Gate 3 | 4K | 104 FPS | 103 FPS |
| Forza Motorsport | 1080p | 254 FPS | 259 FPS |
| Forza Motorsport | 1440p | 212 FPS | 216 FPS |
| Forza Motorsport | 4K | 142 FPS | 143 FPS |
In modern engines optimized for multi-threading, AMD’s architectural improvements begin to show clear advantages. For gamers who also stream or multitask during gaming sessions, the Ryzen 9 9950X offers better consistency and fewer frame drops under load compared to the hybrid structure of the Intel Core i9-14900K.
Productivity and Multitasking Performance
When it comes to heavy productivity workloads, the Ryzen 9 9950X shines. Applications like Blender, Adobe Premiere Pro, DaVinci Resolve, and complex software compilers benefit significantly from AMD’s symmetrical core architecture and larger cache. In multi-threaded benchmarks such as Cinebench R23 and 7-Zip compression tests, the Ryzen 9 9950X outpaces the Intel Core i9-14900K by an average of 12–18%.
Intel’s Core i9-14900K remains a formidable performer in single-threaded applications and lightly threaded workloads. It holds a lead in tasks like certain Photoshop filters, light audio production, and gaming engines that have not yet optimized for massive core counts. However, as software continues to evolve toward better multi-core utilization, AMD's uniform core design provides an increasingly tangible advantage.
For users who split their time between gaming, content creation, and multitasking, the Ryzen 9 9950X is the more future-proof choice.
Thermals and Power Consumption
Thermal and power behavior is another area where the two processors differ dramatically.
The Intel Core i9-14900K can be extremely power-hungry under sustained loads. It has a base TDP of 125W, but under boost conditions (PL2), it can spike up to 253W or even higher in some workloads. This high power draw leads to significant heat output, and without a premium cooling solution — such as a 360mm AIO liquid cooler or custom water cooling — the processor can throttle itself to protect thermals.
The Ryzen 9 9950X, by contrast, maintains a relatively lower power profile, topping out around 170W under full load. While it still requires strong cooling to perform optimally, especially under prolonged workloads, it is easier to manage thermally than the Intel Core i9-14900K.
This translates to quieter systems and potentially longer hardware longevity. If energy efficiency, cooler operation, and system noise are important factors, the Ryzen 9 9950X holds a clear advantage.
Platform and Upgrade Considerations
Choosing between these CPUs also means choosing between two very different platforms.
The Intel Core i9-14900K is compatible with the Z690 and Z790 chipsets, allowing users to save money by reusing DDR4 RAM or upgrading from older 12th/13th Gen systems. Motherboard prices for Intel’s platform are generally lower, and there are plentiful options for every budget.
AMD’s Ryzen 9 9950X uses the AM5 socket with the X870 chipset. AM5 requires DDR5 memory exclusively, which is now more affordable but still generally pricier than DDR4 setups. However, AMD has committed to supporting the AM5 socket for several future CPU generations, making it a more forward-looking investment.
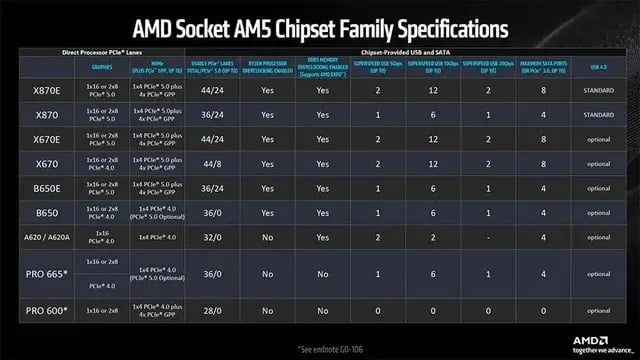
Additionally, X870 motherboards offer more PCIe 5.0 lanes, faster USB4 support, and cutting-edge storage features out of the box.
If you are looking for a short-term upgrade with cost savings, Intel’s Core i9-14900K may be more appealing. If you are building a platform for long-term upgrades and future-proofing, AMD’s Ryzen 9 9950X is the better choice.
Final Verdict
Both the AMD Ryzen 9 9950X and the Intel Core i9-14900K are exceptional CPUs that offer incredible performance for gaming, content creation, and everything in between. However, their strengths are nuanced.
The Intel Core i9-14900K is the choice for those seeking the absolute highest single-threaded performance, the best esports frame rates, and a straightforward upgrade path for existing Intel users. Its raw clock speeds and compatibility with affordable motherboards and DDR4 RAM make it highly competitive.
The AMD Ryzen 9 9950X, however, is the more versatile processor overall. It delivers better multi-threaded performance, superior power efficiency, more stable temperatures, and a more modern platform ready for the next few years of technological advancements. For gamers who also create, stream, or run demanding applications simultaneously, the Ryzen 9 9950X provides a more consistent and efficient experience.
Ultimately, your choice should come down to what you prioritize: peak gaming performance and cost-efficiency with Intel, or all-around superiority and future readiness with AMD.